Mind experiments and creating opportunities in manufacturing Businesses
Do thought experiments help us understand the world? On the basis of at least three different thought experiments, we discuss the strengths and limitations of this method using philosophical background information. Having found these strengths and weakness (limitations) we will extend this question to whether thought experiments can help us in a modern manufacturing business context.
Preface
Introduction
In this philosophical paper, I will address the importance of thought experimentations and the limitations. Three different thought experiments will be given as an concrete example of thought experiments. I will dive into the material from philosophers who have contributed to mind experiments along with additional backgrounds to explain whether thought experiments can help us to understand the world. I believe that the world around us is driven by technology. Moreover, a society is defined by its technological achievements. However, knowledge is becoming widely available due to the internet. Whereas a few hundred years ago knowledge was only obtainable locally through books or expert. Now people can find information on the internet in a snap.
This introduces a few interesting problems to think about: when gaining knowledge there are several methods e.g. looking something up on the internet or experiment yourself. In this sense when not always having the tools around you have to improvise in many situations to gain knowledge.
I will question in this paper whether mind experiments can contribute to understanding of our world in which we live in driven by technology and if we can apply usage for business context such as creating opportunities. I will particularly focus on designing a product or creating out-of-the-box solutions.
Methodology
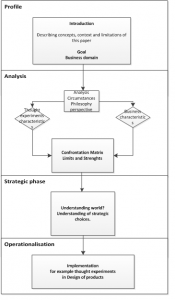
In a SWOT analysis we can combine strengths en weaknesses (internal) from a business and also compare treats and opportunities (external factors). In finding useful information about whether mind experiments can help us in business we are going to analyze common internal and external weakness within businesses. I will use for this methodology an analysis of internal strength en weaknesses in today’s businesses by looking at the role of physical-technical and social factors in design . Once we have found common strength en weakness we can combine them with characteristics of mind experiments. Due to the nature of an mind experiment I propose that a mind experiment can be seen as a ‘virtual’ (external) asset. There for we can characterize them with opportunities and threats which we can combine in a SWOT model. Ultimately, I will confront the strength and weakness with the opportunities and treats of mind experiments (confrontation matrix) so that they can maybe give us powerful insight of using thought experiments as a way of not achieving practical knowledge, but also gaining creativity or understanding our world better. This above introduction leads us to the below questions.
Our main research question is
Q.1 Do thought experiments help us understand the world and can they contribute to business?
On the basis of at least three different thought experiments, we discuss the strengths and limitations of this method. Mind experiments differ quite from thinking in ‘words’ so I first will address some limitations in thinking only in words and what kind of limitation this leads us too. Secondly, I will dive into thought experiments.
Sub question two can now be formulated
What are thought experiments? (we are looking here for concepts, descriptions, methods)
- I give three example thought experiments, using material on philosophers and their view on thought experiments.
- Which philosophers (may have) contributed to the concept of thought experiment’s? What were their characteristics and perspective?
- Example of thought experiments that may have contributed to the understanding of our world?
- Once we have the characteristics I will explain and discuss the strengths and limitations of this method.
- Strength: does it actually contributes to the user or anyone who participate in thought experiments in general?
Q.2 Business case
Once we have found out strengths and limits we can confront them with common business problems. I will combine theory mentioned in Philosophy of Technology by Pieter Vermaas and give pre-assumptions about strength and weaknesses in business.
Confronting strengths and limitations in business will lead us: How can we use thought experiments in business?
Below is the full operationalization proposal which should form an analysis framework to find out whether mind experiments can contribute. I will explain strategic choices and operationalization for manufacturing companies.
1. Philosophers and thought experiments history
According to Boorsboom et all (2002) et all thought experiments can fulfill a specific function within theory but quite often they are used because it is impossible to run an experiment in a real world scenario.
We visualize a certain situation and think of a important operation, this allows us to raise new questions (and we see what happens) and we draw a conclusion.
We can classify thought experiments for convenience by the type of use. There are multiple types of thought experiments but the main division is destructive vs. constructive.
In the case for destructive most of the time thought experiments draw out a contradiction in theory, thereby refuting it. A second type is that thought experiments aim to show that theory in question cannot be merged with other theories. For example mind experiments about paradoxes. There is also a third type of negative thought experiment where a central thought of the thought experiment itself is undermined. Last we have a counter thought experiment which tries to find arguments why a though experiment would not work.
Karl Popper however has distinguished three types of thought experiments. Heuristic (which is meant to illustrate a theory) Critical (against a theory) and apologetic (in favor of a theory).
Through history it is very much likely that since the time of the Pre-Socratics thought experiments have been practiced. They emphasized thought experimentation as a cognitive procedure and practiced it with great dedication and versatility.” Moreover, it seems that medieval science relied rather on thought experiments than real-world experiments (King, 1991).
The 17th century saw some of its most brilliant practitioners in Galileo, Descartes, Newton, and Leibniz And in our own time, the creation of quantum mechanics (see Kühne, 2005, pp. 280–317) and relativistic physics (see e.g. Brown, 1987) are almost unthinkable without the crucial function of thought experiments.
1.2. Analysis three cases of thought experiments and their characteristics
I have selected three thought experiments to use in the case. I will explain the thought experiments and sum up strengths and limitations. I have chosen thought experiments from different kinds of categories such as physics, mathematics and ethical thought experiment so that any judgment is not based on thought experiments from selecting one kind of category.
The infinite monkey theorem (mathematics)
The infinite monkey theorem is a thought experiment where we imagine a situation where we have an infinite number of monkeys to hit random keys on an infinite number of typewriters for an infinite amount of time. Now imagine the monkeys doing this. The above picture illustrates this, then at some point it is stated that they can produce the complete works of Shakespeare.
This idea was popularized in the early 20th century by Emile Borel, a French mathematician.
What is the purpose of this thought experiment?
This thought experiment addresses well the nature of infinity. For many people it is hard to get a grasp on what infinity means or what it can produce. In this experiment the ‘random function’ is also very important. The random function is here illustrated with the monkeys typing random keys. (They produce letters and symbols at random).
This thought experiment helps to illustrate the possibilities of a simple concept and what will produced.
Note that the possibility would be very small to have the entire work of Shake Spear created in the real world. In 2003 science students in the UK tested the infinite monkey theorem when they put a computer and a typewriter in the zoo, allowing primates to type on it. Unfortunately the primates were only able to produces a few pages with the letters on it. Although in real world not possible, further research was done and with computer simulator (software) it was actually possible to get a sentence produced. (We talk here about recreating infinite time and infinite monkeys and infinite random typing by using a software which can simulate monkey randomly typing)
Strengths in the infinite monkey theorem
In this experiment it is easy to imagine what a world of infiniteness may produce
The monkey is here a replacement for an abstract device that produces an endless random sequence of symbols and letters. (think of a random function in a computer but infinite)
ü It therefor has the benefit of reduce complexity to something simple.
They replace function (random) by something people can imagine.
ü Everything is possible with when we have infinite time and infinite random access to a production of randomness in any form.
Although this seems as an eye-opener we will further use this strength later on.
Limitations in the infinite monkey theorem
Limitations in this experiment are for example the scenario of monkeys actually writing or producing something. It was interesting that the experiment was tried in real life (and did not work) therefor this thought experiment should only be used for it function namely explain the effect of infinity and random producing.
- Should be use according it function what it tries to explain, imaginary it works, when tried in reality not. You should then substitute or simulate.
The Spider in the Urinal (ethics)
The spider in the urinal is a somewhat disturbing thought experiment. It was introduced in the essay of Thomas Nagel (1986) “Birth, Death and the meaning of life”. It describes the issues of non-interference and the meaningfulness of life. He gained a new insight when he saw a sad little spider living in the urinal of a men’s bathroom at the Princeton. The spider was obvious peed on sitting there in the urinal and Nagel thought that he could make his life happier by giving him another habitat outside the urinal. (Because he was trapped by the smooth surface of the porcelain and the wide overhang). There was obvious no way that he could tell that he wanted to go out, but life inside the urinal did look awful according Nagel.
So one day at the end of the term he took a paper towel and extended it to the little spider. The spider gasped with his legs on the towel and he put the spider on the floor.
Thinking that he would be fine now, the spider just sat there without moving a muscle. Nagel nudged him a bit with the towel but still nothing happened. When Nagel came back after a couple of hours he still hadn’t moved.
The next day Nagel found him at the same place his legs shriveled in the way of characteristic of dead spiders. His corpse laid there for a while after he finally got swept away.
Strengths The Spider in the Urinal
This thought experiment focuses on the quality of animal lives but also forces us to think of our own life’s. The thought experiment was meant to express that it is highly debatable what anyone really wants. (you can never surely know). Secondly, how do our lives do any other good?
- This thought experiment allows us to experiment with policies of intervention. We might have best intentions but interference can sometimes inflict harm.
- Sometimes inaction can be morally problematic.
This thought experiment forces us to consider the quality and meaningfulness of not just animal lives, but our own as well. How can we ever know what anyone really wants? And do our lives actually do us any good? It also forces us to question our policies of intervention. Despite our best intentions, interference can sometimes inflict unanticipated harm.
Limitations
This is quite an interesting thought experiment since it has a small contrast with real life situation. The thought experiment is derived from something that can actually happen, whether it is a spider or something else. However in this case there might be an inaccurate problem of selecting the problem itself. The spider was in this case found dead but it was not told if someone stepped on him, not splashing him but accidentally squashed him a little bit and therefor he died the next day. So there is a problem of selecting here but again for the purpose of explaining Nagel used this as an concrete example.
- Selection problem
Newton’s canon ball (physics)
The newton’s cannonball (Principia Mathematica) is a thought experiment in physics which visualizes how a cannon ball can get into orbit around earth. The experiment illustrates a canon from the top of a mountain which fires a cannonball at a certain speed.
Now if we assume that there are no other forces such as gravitation or air resistance then in theory the cannonball should follow a straight line in the direction it was fired (away from earth).
However, if the gravitational force acts on the fired cannonball it will of course follow a different path depending on its initial velocity. In addition to that if the speed is too low then the cannonball will fall back to earth.
Now imagine that the initial speed is higher than the orbital velocity, but not high enough to leave earth altogether (lower than the escape velocity) it will continue revolving around earth and it will enter an elliptical orbit.
If the speed is low, it will simply fall back on earth.
Strengths of Newton’s cannonball
This thought experiment combines real world physics with objects that are imaginary. A canon ball will never shoot a ball at the speed so that it will leave the earth atmosphere. But the imaginary function of that it can is very powerful. Newton did not limit himself to technology that wasn’t there yet, but thought of “what if” the technology was there. It is therefore an extension of what could be there and a motivation to assume that an object will fall into an elliptical orbit.
The Newton’s cannon ball will later be a good concept of shooting satellites into orbit so the model proves to be handy even a few hundred years later.
- Although speed couldn’t be measured at the time the model shows us that by variation of speed the elliptical orbit could be determined.
- Although technology did not exist for shooting anything into space basic behavior of objects were explained (elliptical orbit)
Limitations
- The model illustrates the orbit but not the calculations which is obvious but a strength and a weakness. It is a great example of the “aha” effect without showing actual math.
Conclusion
From here we can ask ourselves do thought experiments help us understand the word?
Well I think they can. They can help us understand the world without having to know everything. The mind simply fills in what concepts may apply. From a language and problem solving perspective Philosophers see a proper understanding in our language as the key to solve many philosophical problems which I think is an important thing when using mind experiments.
These problems were mainly focused on what is the nature of meaning? Or e.g. what is the relation between language and reality? However they also emphasize what the relation is between language and thought (cognition) and what is the relation between meaning and use or meaning and context in language. Therefor interpretation about the world is also constituted in language and thought experiments help us to understand the world.
Frege (1948-1925) and Russell tried to analyze phrases in natural languages into a formal logic.
While this essay on thought experiments does not focus on the logic of natural languages, I do want to point out that language can be seen as important to express the relation between language and reality and thought experiments using both, in other words language and thought can be assumed to be conflated to express the world so they help us understand the world.
Having said this, there are many ways how we can describe our world and the nature of things. For example we can simply describe our world with “words, sentences, languages” but from here we learned that there are also other ways such as graphics and context and also in addition we can have ‘though experiments’.
When we look at problem solving we can use logic. However, there is a difference in everyday reasoning and the logical systems devised from logicians. A great deal of everyday thinking is practical, intuitive and emotional whereas thinking in formal logic requires a lot more training and is therefore less intuitive.
Now that we have found strengths and weaknesses or (limitations) I ask myself whether these strengths can be useful in business. Manufacturing companies tend to have difficulties in creating innovative solutions or products which is introduces in the first part of this paper. As today’s society is strongly technology I would like to know how thought experiments may help us with problem solving in a philosophical context but also in business context for example in product design and manufacturing. Below is a summary of the results that we have found until here:
Opportunity
- It therefor has the benefit of reduce complexity to something simple.
- They replace function (random) by something people can imagine.
- Everything is possible with when we have infinite time and infinite random access to a production of randomness in any form.
- This thought experiment allows us to experiment with policies of intervention. We might have best intentions but interference can sometimes inflict harm.
- Sometimes inaction can be morally problematic.
- Although speed couldn’t be measured at the time the model shows us that by variation of speed the elliptical orbit could be determined.
- Although technology did not exist for shooting anything into space basic behavior of objects were explained.
Treats
- Should be use according it function what it tries to explain, imaginary it works, when tried in reality not. You should then substitute or simulate
- Selection problem
- The model illustrates the orbit but not the calculations which is obvious but a strength and a weakness. It is a great example of the “aha” effect without showing actual math.
2 Product Design philosophy
This part will look briefly to problems in designing products and manufacturing problems. I look at factors a stated in philosophy of technology from technical artifacts to social technical. The below figure illustrates that there is tension between physical-technical and contextual boundary conditions.
As Pieter Vermaas et all (2011) states requirements have to be the primary function of an technical artifact, the use, production, maintenance, market (price), financing technical standards and norms. Etcetera.
Also he states that what lies hidden behind each of these boundary conditions are the respective interested parties (stakeholder).
Obviously, we cannot look at all factors involved in business therefor I look at the most valuable factor which is creating competitive advantage.
As mentioned in the introduction knowledge becomes more obtainable through internet. Therefor I think that there is a swift in applying this knowledge. Manufactures are characterized mostly depended on resources to in order to manipulate and object (designing). In other words without any resources a company cannot sell. This leads to a weakness of production companies. Secondly financial weakness are very common. In order to manufacture goods a company has to buy these resources such as equipment, assets, facilities and materials to operate. Activities have to be therefore sufficient to operate your business in order to pay loans or doing business .
High costs of doing business and limited cash flow are among common financial weaknesses. In some industries, you need expensive equipment, assets, facilities and materials to operate. A lack of access to loans or equity investments is a related weakness. If your business activities don’t generate substantial monthly cash inflow to overcome your costs of doing business, you face a major uphill climb in generating profit. Some companies struggle therefor with quality issues or having enough (technological) know how. Outdated technology can inhibit innovation and design and prevent designers from differentiating products that will stand out from competitors.
However, in many manufacturing industries markets have to be stable , although demands can highly fluctuate with ups and downs of the economy.
Production inefficiencies are also very important to keep in mind. Production has to be efficient and optimized to make profit. A weakness of low productive can be improved with staff motivation and more efficient equipment or production processes.
Last but not least we find poor brand image. If your brand is considered weak you will not gain lot attention in media and it is difficult to generate sales activity. A poor brand can for example result from a poor design or service, lack of market budget or poorly promotional strategies.
Overall we can state the below four weaknesses
- Financial Weaknesses
- Quality Concerns
- Production Inefficiencies
- Poor Brand Image
3. Operationalization and conclusion
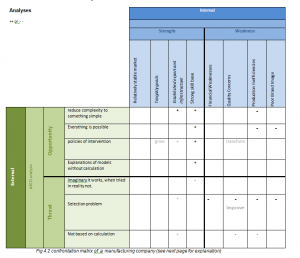
Having addressed the strengths and weaknesses of manufacturing business we can combine them with logics to create strategies. In a confrontation matrix we can combine the strengths weakness and threats and opportunities. By using the SWOT we can construct the confrontation matrix in order to build new strategies. Rolf Oostra, S. S. (2006)
These strategies are formed by below combinations according Rolf Oostra.
- (weakness + threat ) = strategy to improve
- (weakness + opportunity) = strategy to transform
- (strength + opportunity) = strategy to grow
Implementing the strategies
Through this paper we have found different kinds of strengths and limits of mind experiments, but arguments can be combined to create business opportunities. This follows out the confrontation matrix.
For example in the thought experiment of the infinite monkey theory complexity is reduced to something simple. This can be perfectly combined with a strength such as strong skill base, by focusing on reducing complexity in thinking and also having the assumption that “everything” is possible companies can think “out of the box”. This seems to be a very obvious statement however many companies do not apply these thoughts therefor not creating unique products as mentioned before which can heavily reduce quality. Also policies of invention help us to react fast, combined with skills this can be a good strategy to grow. Last but not least having to reduce calculations in manufacturing (elimination for example risk management) you can focus on creating skill and new ways to grow.
When we look at transforming strategies though experiments we can combine production efficiencies with everything is possible concept. This is a perfect combination of transforming the production process, eliminating possible factors which can hold up production. By not looking at what is impossible but focus on processes it allows the question “what if”. For example imagine a company producing electric cars and people say we don’t have the technology to produce cars that can have long distance due to battery efficiency. Then the company can decide to just manufacture the car anyway assuming that the technology will be ready later to travel long distances. In this way the company can gain competitive advantage by thinking ahead of its competitors. While everybody else is tackling the long distance problem). This show that also mind experiments can lead companies forward and allow them to transform quickly.
Last but not least quality concerns production inefficiencies , poor branding can be due to selecting problems which can form a threat. In this case a strategy would be to improve concepts an look at how selection is made in ideas of the company. Assumption therefor always need to be improved.
In this essay I have tried to explain that thought experiments can help us understand the world by focusing on experiments in thoughts and therefor creating valuable assets by combining concepts of mind. I also would like to emphasize to my view that thought experiments can be essential not only in understanding the technological world around us but also can be useful in manufacturing businesses to think for example “out of the box”. They form possible building blocks to grow allowing a company to improve, transform or grow which is a very powerful way of thinking, creating and generating new ideas even in a business context.
Literature
Frege and Russell. Retrieved 22 October, 2013 from http://www.iep.utm.edu/lang-phi/#H1
Vermaas, Pieter et all (2011) A Philosophy of Technology- From artifacts to Sociotechnical systems, Morgan & Claypool Publishers
René Descartes (1596—1650): Overview. Retrieved 22 October, 2013 from http://www.iep.utm.edu/descarte/
Thought Experiments. Retrieved 22 October, 2013 from http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/thought-experiment/
Top 10 Most Famous Thought Experiments. Retrieved 12 October, 2013 from http://www.toptenz.net/top-10-most-famous-thought-experiments.php
T. Nagel, the view from nowhere,1987,Oxford university press.
Gravity and Newton’s Cannon. Retrieved 22 October, 2013 from http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/gravity_newtons_cannon.htm
SWOT Analysis of Manufacturing Industry. Retrieved 8 November, http://www.ehow.com/about_6767951_swot-analysis-manufacturing-industry.html#ixzz2kHCjszZ3
Examples of Company Weaknesses . Retrieved 3 November, 2013 http://smallbusiness.chron.com/examples-company-weaknesses-69993.html
Pre-Logic, Formal Logic, Dialectical Logic, Retrieved 8 November http://www.marxists.org/reference/archive/hegel/txt/system2.htm
Rolf Oostra, S. S. (2006). Handboekstrategische Marketing. Utrecht/Zutphen: ThiemeMeulenhoff.